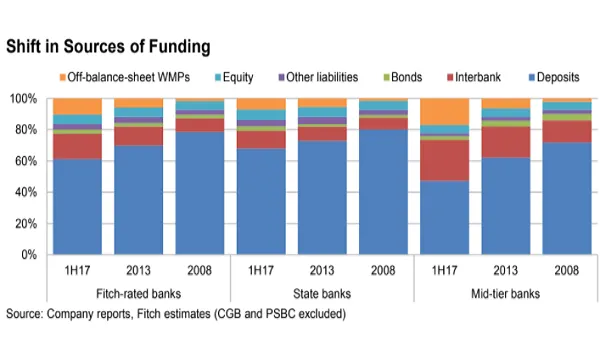
Chart of the Week: Check out how China banks' funding profiles have evolved
Off-balance-sheet WMPs filled the gap between assets and deposits.
According to Fitch Ratings, since 2008, China has moved away from having limited investment alternatives, strict caps on deposit rates and loan-to-deposit ratios as well as very high economic growth – all of which contributed to banks being flush with deposits – and towards increasing diversification of investments and funding in an environment of slower growth and margin pressure. The pace of expansion in loans and other forms of credit now regularly exceeds deposits.
Here's more from Fitch:
Among Fitch-rated commercial banks, customer deposits accounted for 61% of total equity and liabilities (including WMPs, which we treat as contingent liabilities) at end-1H17, down from 70% and 78% at end-2013 and end-2008 respectively. The graph shows that the widening gap between assets and deposits has been filled chiefly by off-balance-sheet WMPs and interbank borrowing; the latter includes funds provided by the PBOC and other banks via placements and repurchase agreements. Mid-tier banks are especially reliant on these sources of funding.
We estimate that off-balance-sheet WMPs and interbank borrowing made up 43% of mid-tier banks’ funding as of end-1H17 (state-banks: 19%), contributing to their asset-liability mismatches. In 2017, mid-tier banks also increasingly turned to negotiable certificates of deposits (CDs) because of funding squeezes elsewhere in the money market (WMP balances have also reduced), with the average CD auction rate exceeding 5% in June 2017.
The proportion of foreign-currency wholesale funding has not increased significantly despite an expansion in international activities, although the proportion may rise if the larger commercial banks continue to rapidly expand their offshore operations. For Fitch-rated commercial banks, foreign-currency liabilities increased to 11% of total liabilities from 9% in the past three years, and foreign-currency non-deposit liabilities increased to 4% of total liabilities from 3%.

















 Advertise
Advertise











